How do you create a 3D model of a historic graveyard? With eight Raspberry Pi computers, as Rob Zwetsloot discovers in the latest issue of The MagPi magazine, out now.
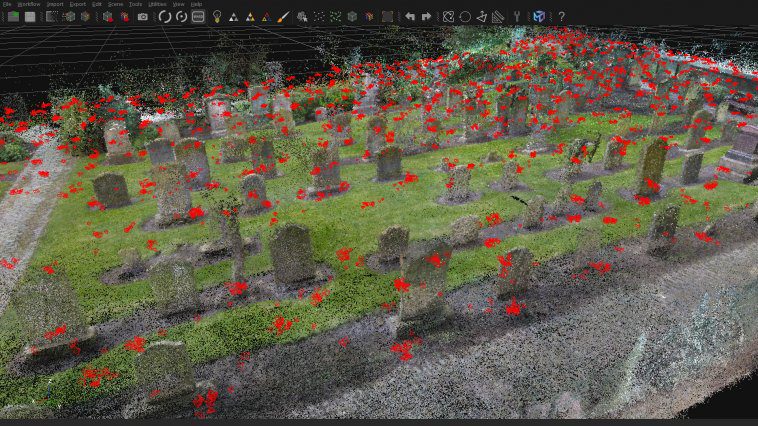
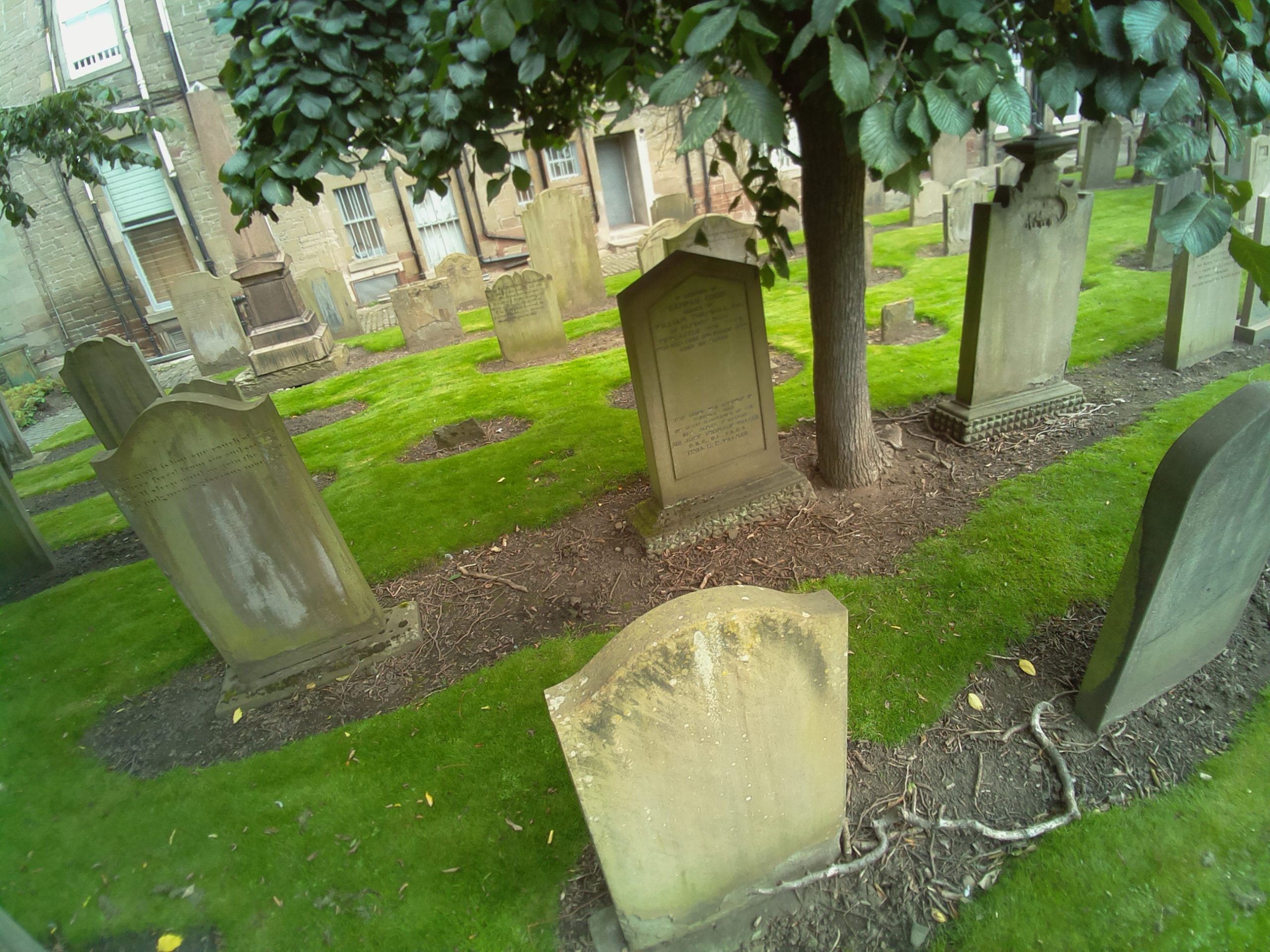
“In the city centre of Dundee is a historical burial ground, The Howff,” says Daniel Muirhead. We should probably clarify that he’s a 3D artist. “This old graveyard is densely packed with around 1500 gravestones and other funerary monuments, which happens to make it an excellent technical challenge for photogrammetry photo capture.”
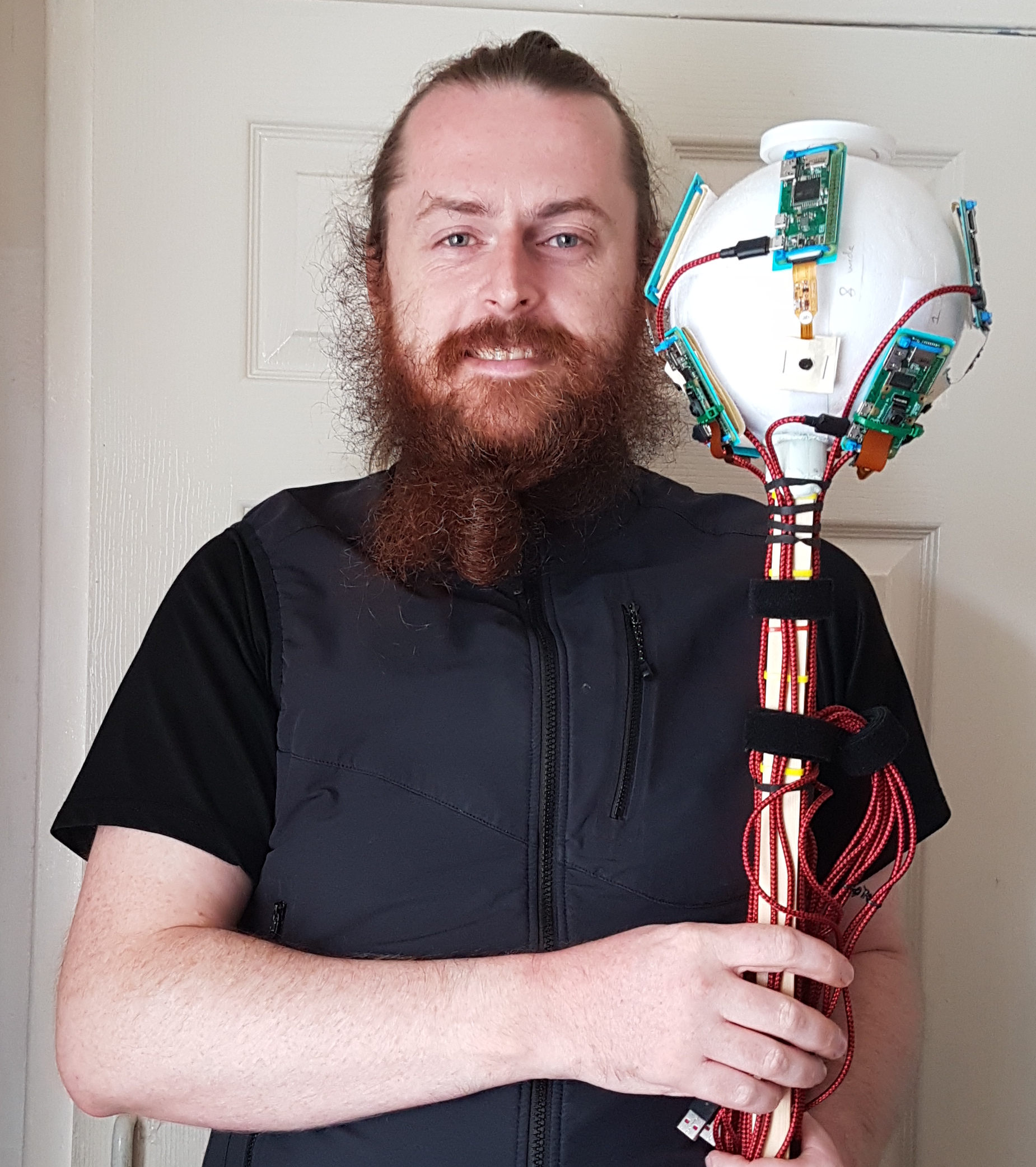
This architecture, stone paths, and vibrant flora is why Daniel ended up creating a 3D-scanning rig out of eight Raspberry Pi computers. And the results are quite stunning.
“The goal of this project was to capture photos for use in generating a 3D model of the ground,” he continues. “That model will be used as a base for attaching individual gravestone models and eventually building up a full composite model of this complex subject. The ground model will also be purposed for rendering an ultra-high-resolution map of the graveyard. The historical graveyard has a very active community group that are engaged in its study and digitisation, the Dundee Howff Conservation Group, so I will be sharing my digital outputs with them.”
Google graveyard

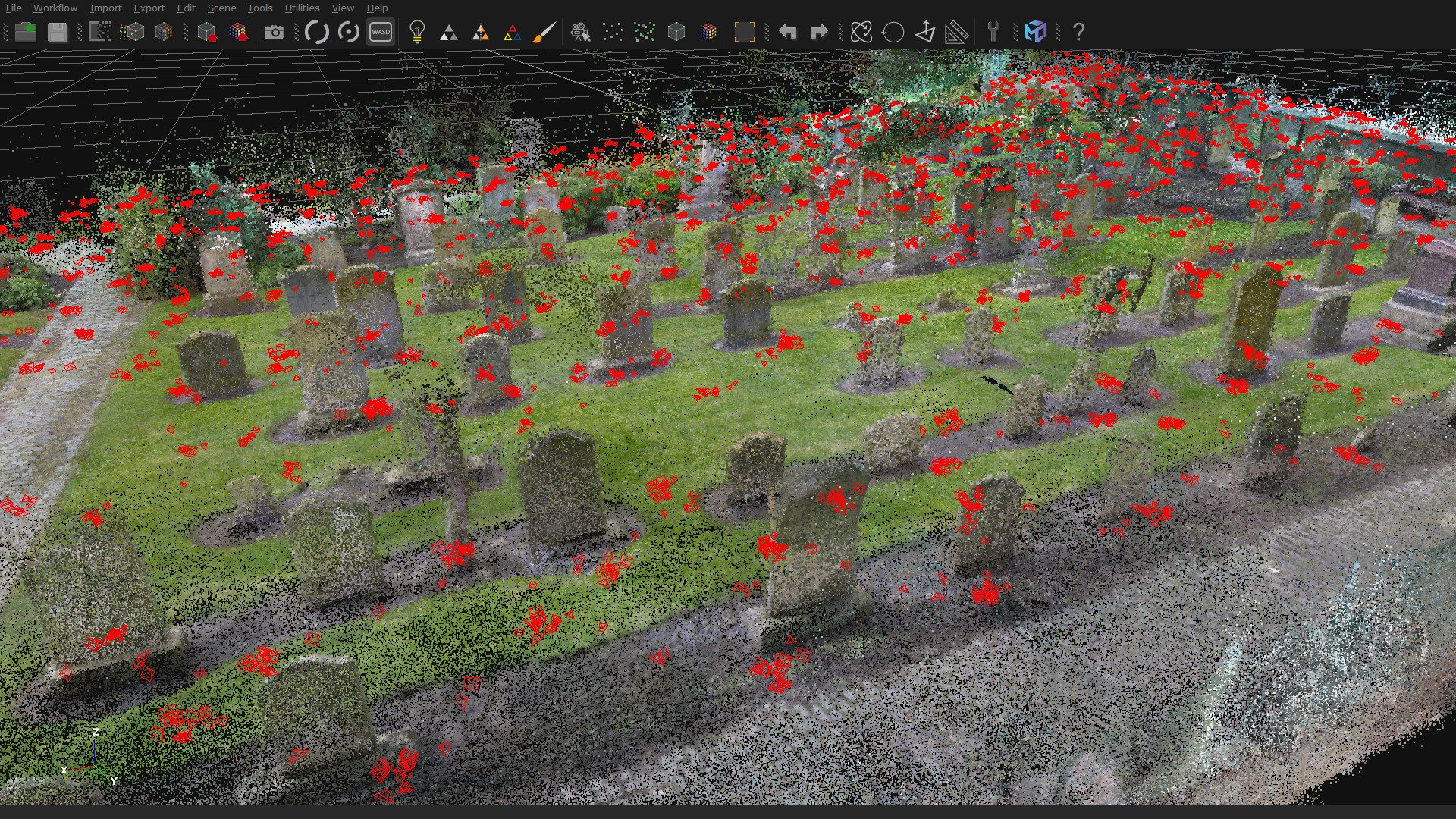
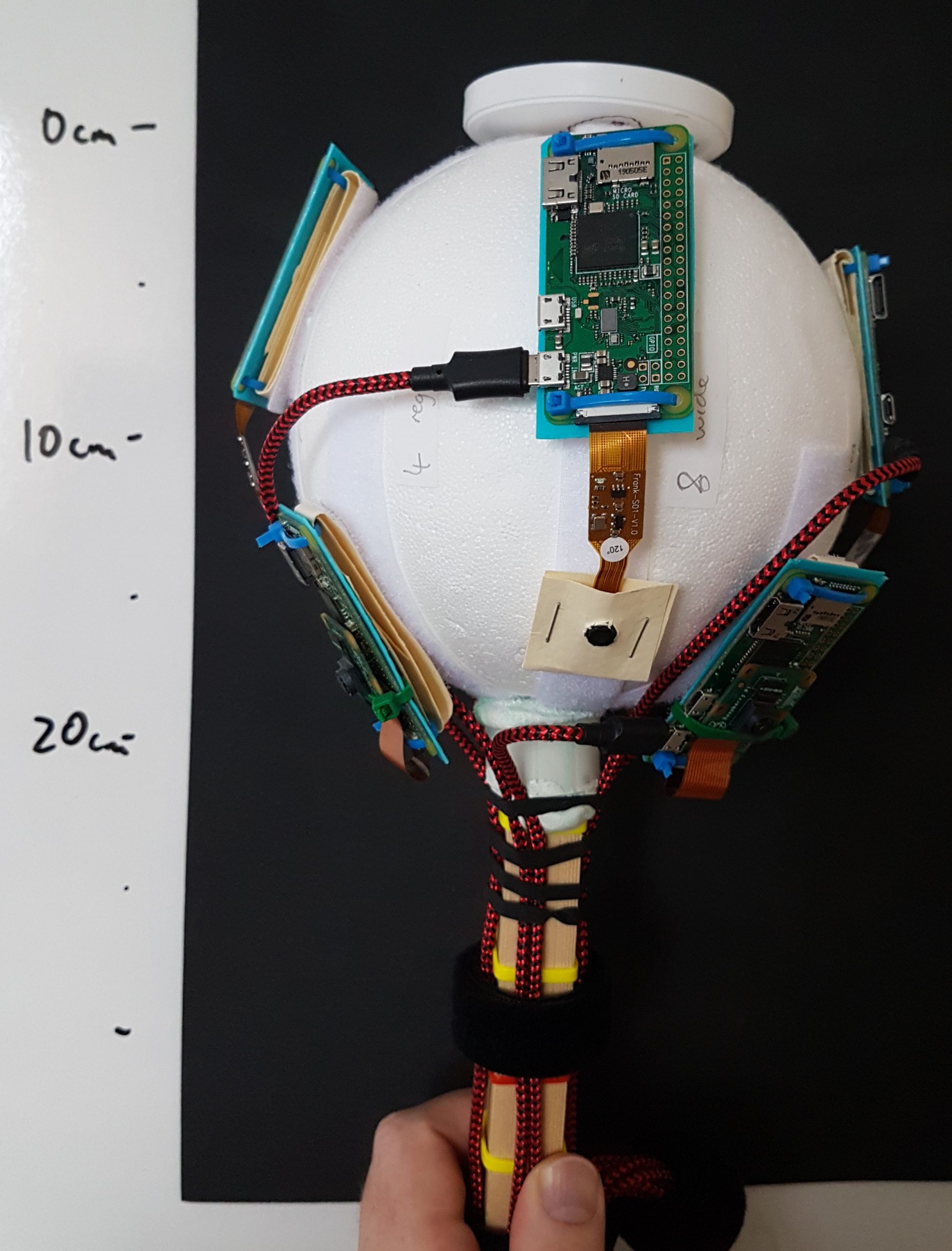
To move the rig throughout the graveyard, Daniel used himself as the major moving part. With the eight Raspberry Pi cameras taking a photo every two seconds, he was able to capture over 180,000 photos over 13 hours of capture sessions.
“The rig was held above my head and the cameras were angled in such a way as to occlude me from view, so I was not captured in the photographs which instead were focused on the ground,” he explains. “Of the eight cameras, four were the regular model with 53.5 ° horizontal field of view (FoV), and the other four were a wide-angle model with 120 ° FoV. These were arranged on the rig pointing outwards in eight different directions, alternating regular and wide-angle, all angled at a similar pitch down towards the ground. During capture, the rig was rotated by +45 ° for every second position, so that the wide-angles were facing where the regulars had been facing on the previous capture, and vice versa.”
Daniel worked according to a very specific grid pattern, staying in one spot for five seconds at a time, with the hopes that at the end he’d have every patch of ground photographed from 16 different positions and angles.

“With a lot of photo data to scan through for something fairly complex, we wondered how well the system had worked. Daniel tells us the only problems he had were with some bug fixing on his code: “The images were separated into batches of around 10,000 (1250 photos from each of the eight cameras), plugged into the photogrammetry software, and the software had no problem in reconstructing the ground as a 3D model.”
Accessible 3D surveying
He’s now working towards making it accessible and low-cost to others that might want it. “Low-cost in the triple sense of financial, labour, and time,” he clarifies. “I have logged around 8000 hours in a variety of photogrammetry softwares, in the process capturing over 300,000 photos with a regular camera for use in such files, so I have some experience in this area.”
“With the current state of technology, it should be possible with around £1000 in equipment to perform a terrestrial photo-survey of a town centre in under an hour, then with a combined total of maybe three hours’ manual processing and 20 hours’ automated computer processing, generate a high-quality 3D model, the total production time being under 24 hours. It should be entirely plausible for a local community group to use such a method to perform weekly (or at least monthly) 3D snapshots of their town centre.”
The MagPi issue 99 – Out now

The MagPi magazine is out now, available in print from the Raspberry Pi Press onlinestore, your local newsagents, and the Raspberry Pi Store, Cambridge.
You can also download the PDF directly from the MagPi magazine website.
Website: LINK