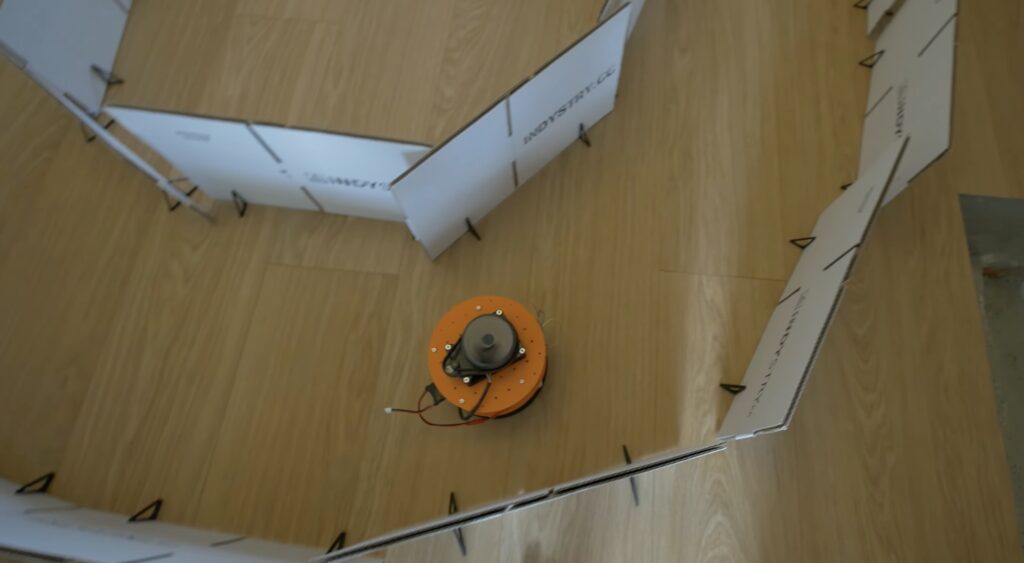
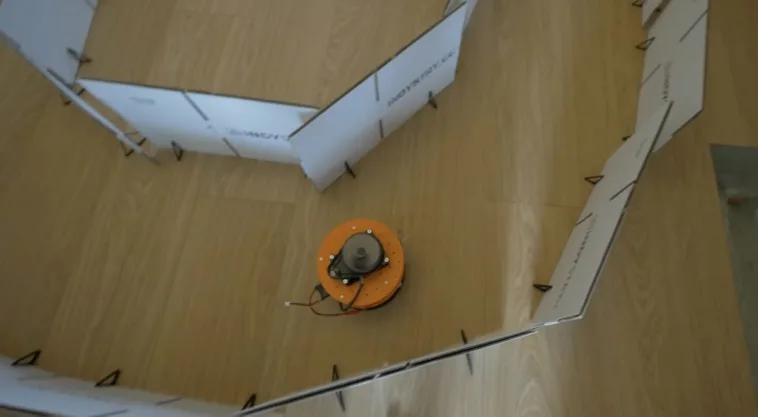
The rapid rise of edge AI capabilities on embedded targets has proven that relatively low-resource microcontrollers are capable of some incredible things. And following the recent release of the Arduino UNO R4 with its Renesas RA4M1 processor, the ceiling has gotten even higher as YouTuber Nikodem Bartnik has demonstrated with his lidar-equipped mobile robot.
Bartnik’s project started with a simple question of whether it’s possible to teach a basic robot how to make its way around obstacles using only lidar instead of the more resource-intensive computer vision techniques employed by most other platforms. The chassis and hardware, including two DC motors, an UNO R4 Minima, a Bluetooth® module, and SD card, were constructed according to Open Robotic Platform (ORP) rules so that others can easily replicate and extend its functionality. After driving through a series of courses in order to collect a point cloud from the spinning lidar sensor, Bartnik imported the data and performed a few transformations to greatly minify the classification model.
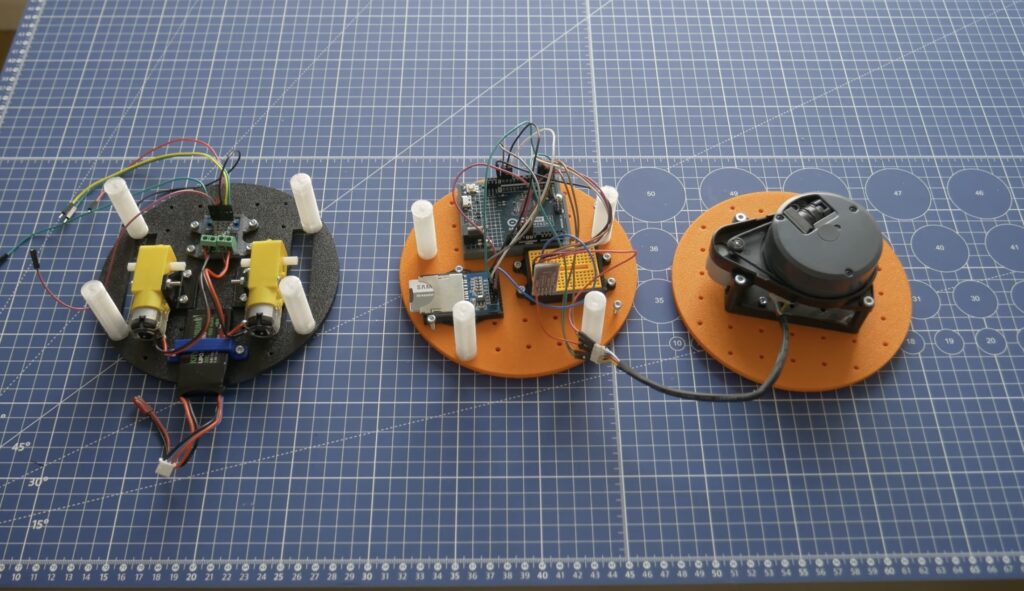
Once trained, the model was exported with help from the micromlgen Python package and loaded onto the UNO R4. The setup enables the incoming lidar data to be classified as the direction in which the robot should travel, and according to Bartnik’s experiments, this approach worked surprisingly well. Initially, there were a few issues when navigating corners and traveling through a figure eight track, but additional training data solved it and allowed the vehicle to overcome a completely novel course at maximum speed.
The post Teaching an Arduino UNO R4-powered robot to navigate obstacles autonomously appeared first on Arduino Blog.
Website: LINK


